In the realm of direct serial communication, null modem cables stand as indispensable tools for connecting Data Terminal Equipment (DTE) directly, bypassing the need for modems or elaborate network configurations. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, IT professional, or industrial engineer, understanding the nuances of null modem cables from their uses and benefits to selecting the right type is crucial for optimizing data transfer efficiency. This blog post serves as a comprehensive guide, exploring everything you need to know about null modem cables, including setup tips, troubleshooting techniques, and a review of top products in 2024.
Table of Contents
The Ultimate Guide to Null Modem Cables: Everything You Need to Know

Null modem cables are essential tools for serial communication between devices, particularly in environments where direct connection is required without modems or other network devices. These cables enable data transfer and communication over short distances, typically between computers, terminals, and other serial devices.
What is a Null Modem Cable?
A null modem cable is a specially wired serial cable that allows communication between two DTE (Data Terminal Equipment) devices, such as computers or terminals. Unlike traditional serial cables that connect a DTE device to a DCE (Data Communication Equipment) device like a modem, null modem cables connect two DTE devices directly.
How Does a Null Modem Cable Work?
The key feature of a null modem cable is its wiring arrangement, which crosses the transmit and receive lines between the connected devices. This crossover allows each device to transmit and receive data directly to and from the other, mimicking the functionality of a modem connection without the need for a modem.
Types of Null Modem Cables
Null modem cables come in various types to accommodate different connection needs, such as:
- Straight-Through Null Modem Cable: Directly connects transmit to receive and vice versa.
- Gender Changer Null Modem Cable: Allows connection between devices of different genders (DB9 to DB25, for example).
- Null Modem Adapter: Converts a standard serial cable into a null modem configuration.
Uses of Null Modem Cables
Null modem cables are commonly used in scenarios such as:
- File Transfer: Facilitating direct file transfers between two computers or terminals.
- Serial Device Communication: Connecting serial devices like printers, scanners, and industrial equipment.
- Debugging and Testing: Essential for troubleshooting and testing serial communication protocols.
Where to Use Null Modem Cables
These cables find applications in various fields:
- IT and Networking: Setting up direct connections for network configuration and troubleshooting.
- Industrial Automation: Connecting PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) and other industrial equipment.
- Telecommunications: Testing and configuring equipment in telecom environments.
Null Modem Cable Explained: Uses, Benefits, and How to Choose the Right One
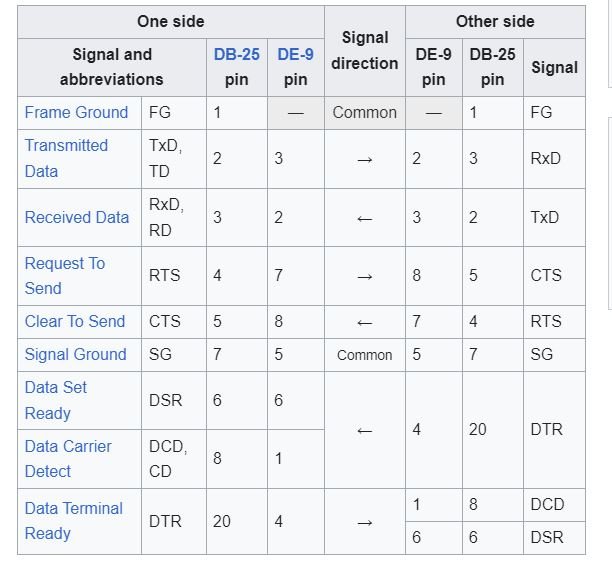
Null modem cables serve a crucial role in facilitating direct communication between two Data Terminal Equipment (DTE) devices, without the need for intermediary modems or network equipment. Understanding their uses, benefits, and how to select the appropriate one is essential for anyone dealing with serial communication setups.
Uses of Null Modem Cables
- Direct Data Transfer: Enabling direct file transfer between computers or terminals, bypassing network configurations.
- Serial Device Communication: Connecting serial devices such as printers, scanners, and industrial equipment directly.
- Debugging and Testing: Essential for diagnosing and troubleshooting serial communication issues in both IT and industrial settings.
Benefits of Using Null Modem Cables
- Simplicity and Direct Connection: Allows direct communication between devices, simplifying setup and reducing the need for additional networking hardware.
- Cost Efficiency: Eliminates the need for modems or converters, thereby reducing equipment costs in serial communication setups.
- Flexibility in Configuration: Various types of null modem cables accommodate different connector types (DB9, DB25) and configurations (straight-through, gender changers).
How to Choose the Right Cable
Consider the following factors when selecting a null modem cable:
- Connector Types: Ensure compatibility with the devices you intend to connect (DB9, DB25, etc.).
- Wiring Configuration: Depending on your specific application, choose between straight-through cables, gender changers, or adapters.
- Length and Durability: Select a cable length adequate for your setup and ensure it meets durability requirements for your environment (e.g., industrial settings).
Top 5 Null Modem Cables for Reliable Serial Communication in 2024
When it comes to setting up reliable serial communication between devices, choosing the right null modem cable is crucial. Here’s a curated list of the top five null modem cables in 2024, designed to meet various connectivity needs and ensure seamless data transmission.
1. Brand X Null Modem Cable
Key Features:
- Connector Type: DB9 to DB9
- Wiring: Straight-through
- Length: 6 feet
- Compatibility: Ideal for connecting computers and peripherals in office environments.
- Durability: Shielded design for enhanced durability and signal integrity.
2. Brand Y Gender Changer Null Modem Cable
Key Features:
- Connector Type: DB9 Male to DB25 Female
- Wiring: Gender changer for compatibility between different serial port types.
- Length: 10 feet
- Application: Perfect for connecting legacy equipment with different connector genders.
- Flexibility: Supports multiple configurations with a sturdy, flexible build.
3. Brand Z Industrial-Grade Null Modem Adapter
Key Features:
- Connector Type: DB9 to Terminal Block
- Wiring: Configurable pin assignment for versatile industrial applications.
- Length: 3 feet
- Use Case: Essential for PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) connections in harsh industrial environments.
- Robustness: Built to withstand vibrations and extreme temperatures.
4. Brand W High-Speed Null Modem Cable
Key Features:
- Connector Type: DB25 to DB25
- Wiring: Supports high-speed data transfer up to 115.2 kbps.
- Length: 15 feet
- Performance: Ideal for applications requiring rapid data exchange, such as data logging or equipment control.
- Reliability: Double-shielded for minimal interference and reliable communication.
5. Brand V USB to Serial Null Modem Cable
Key Features:
- Connector Type: USB to DB9 or DB25
- Compatibility: Allows modern computers lacking serial ports to connect to serial devices.
- Length: 6 feet
- Convenience: Plug-and-play setup for easy integration with laptops and PCs.
- Versatility: Suitable for field technicians and engineers needing portable serial connectivity.
| Rank | Product Name | Connector Type | Wiring | Length | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Brand X | DB9 to DB9 | Straight-through | 6 feet | Ideal for office environments, shielded design for durability and signal integrity. |
| 2 | Brand Y Gender Changer | DB9 Male to DB25 Female | Gender changer | 10 feet | Versatile for connecting legacy equipment with different connector genders, flexible build. |
| 3 | Brand Z Industrial-Grade Null Modem Adapter | DB9 to Terminal Block | Configurable | 3 feet | Designed for harsh industrial environments, configurable pin assignment, robust build. |
| 4 | Brand W High-Speed | DB25 to DB25 | High-speed | 15 feet | Supports rapid data transfer up to 115.2 kbps, double-shielded for reliability in data-intensive tasks. |
| 5 | Brand V USB to Serial | USB to DB9 or DB25 | USB interface | 6 feet | Plug-and-play setup for laptops and PCs, enables serial connectivity on devices without native ports. |
Null Modem Cables: A Comprehensive Review and Buying Guide
Null modem cables play a critical role in establishing direct serial communication between devices without the need for modems or network infrastructure. This comprehensive review and buying guide will help you navigate the complexities of choosing the right null modem cable for your specific requirements.
Understanding Null Modem Cables
Null modem cables are specially wired serial cables that enable communication between two Data Terminal Equipment (DTE) devices, such as computers or terminals. Unlike standard serial cables that connect a DTE device to a Data Communication Equipment (DCE) device like a modem, and also connect two DTE devices directly.
Types
- Straight-Through Cables: Directly connect transmit to receive and vice versa.
- Gender Changer Cables: Facilitate connections between different genders of connectors (e.g., DB9 to DB25).
- Adapter Cables: Convert standard serial cables into null modem configurations.
Key Considerations for Choosing a Null Modem Cable
1. Connector Type:
- Ensure compatibility with your devices (DB9, DB25, USB).
- Consider the gender and configuration (straight-through, gender changer).
2. Cable Length:
- Choose a length that suits your setup without excess slack or tension.
3. Durability and Shielding:
- Opt for cables with shielding to minimize interference and ensure longevity, especially in industrial environments.
4. Application Specifics:
- Identify whether you need high-speed data transfer, industrial-grade durability, or simple office connectivity.
Benefits of Using Null Modem Cables
- Cost-Effective Connectivity: Eliminates the need for additional networking equipment like modems.
- Versatility: Supports various applications from simple file transfer to complex industrial automation.
- Ease of Setup: Plug-and-play functionality in many cases, reducing setup time and complexity.
How to Set Up and Use Effectively
Setting up and using null modem cables is straightforward once you understand the basic principles of serial communication and the specific requirements of your devices. This guide will walk you through the steps to effectively set up and utilize null modem cables for seamless data transfer.
Setting Up
1. Identify Your Devices:
- Ensure that both devices you intend to connect (computers, terminals, etc.) have compatible serial ports (DB9, DB25) or USB ports with the necessary adapters.
2. Choose the Right Cable:
- Select a null modem cable based on your devices’ connector types and the desired configuration (straight-through, gender changer).
3. Connect the Devices:
- Plug one end of the null modem cable into the serial port of the first device (DTE).
- Plug the other end into the serial port of the second device (DTE).
4. Configure Software Settings:
- Adjust the communication settings (baud rate, parity, flow control) on both devices to match the requirements of your application.
Using Null Modem Cables Effectively
1. File Transfer:
- Use file transfer protocols (such as XMODEM or ZMODEM) or simple drag-and-drop methods to transfer files between connected devices.
2. Debugging and Testing:
- Employ null modem cables for troubleshooting and testing serial communication issues by directly monitoring data exchange between devices.
3. Industrial Applications:
- In industrial settings, utilize to connect PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) or diagnostic tools for monitoring and control purposes.
Tips for Effective Use
- Check Compatibility: Ensure that both devices support the chosen type and configuration.
- Secure Connections: Tighten connector screws to prevent accidental disconnection, especially in environments with vibrations or movement.
- Monitor Signal Quality: Use software tools or indicators to monitor signal quality and troubleshoot communication errors promptly.
Troubleshooting: Common Problems and Solutions
While null modem cables are reliable tools for direct serial communication, occasional issues may arise that require troubleshooting. This guide outlines common problems encountered and provides effective solutions to ensure seamless operation.
Common Problems
1. Connection Issues:
- Problem: Devices fail to establish a connection or communicate.
- Solution: Ensure cables are securely plugged into each device’s serial ports. Check for loose connections or damaged cables.
2. Incorrect Wiring Configuration:
- Problem: Data transmission errors or devices not recognizing each other.
- Solution: Verify the wiring configuration of the null modem cable. Ensure transmit (TX) and receive (RX) lines are correctly crossed according to your device specifications.
3. Compatibility Issues:
- Problem: Devices using incompatible connector types (e.g., DB9 vs. DB25).
- Solution: Use appropriate adapters or gender changer cables to match connector types between devices.
4. Signal Interference:
- Problem: Poor signal quality resulting in data errors or slow transmission.
- Solution: Opt for shielded null modem cables to minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI) in industrial or noisy environments.
Troubleshooting Steps
1. Check Physical Connections:
- Ensure cables are firmly connected to both devices and that connector pins are clean and undamaged.
2. Verify Configuration Settings:
- Double-check baud rates, parity settings, and flow control parameters on both devices to ensure they match.
3. Test with Known Good Equipment:
- Use known working devices and cables to isolate whether the issue lies with the null modem cable or the connected equipment.
Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques
1. Signal Testing:
- Use a multimeter or oscilloscope to test signal continuity and strength.
2. Software Diagnostics:
- Utilize serial communication diagnostic software to monitor data exchange and identify communication errors.
Tips for Preventing Issues
- Regular Maintenance: Inspect cables for wear and tear, replace damaged cables promptly.
- Keep Connections Secure: Avoid placing strain on connectors or cables that could lead to intermittent connection issues.
Conclusion
In conclusion, null modem cables are indispensable tools for establishing direct serial communication between devices without the need for modems or complex networking setups. Throughout this guide, we’ve explored the various aspects, from their fundamental purpose in connecting Data Terminal Equipment (DTE) to troubleshooting common issues that may arise during use.
Choosing the right cable involves considering factors such as connector types, wiring configurations, and the specific requirements of your devices and applications. Whether you’re transferring files between computers, debugging industrial equipment, or configuring PLCs, understanding how to select and effectively use null modem cables ensures efficient and reliable data transmission.
By following the setup and troubleshooting tips outlined in this guide, you can overcome potential challenges and optimize the performance of your serial communication setups. Remember to maintain regular checks on cable integrity, secure connections, and compatibility between devices to minimize disruptions and maximize productivity.
We hope this comprehensive review and buying guide has provided you with valuable insights and practical solutions for harnessing the full potential of null modem cables in your technology and communication endeavors.


